Storage Targets
MicroStream supports a variety of storage targets. Through an abstracted file system (AFS), it is possible to connect to a lot of different back ends. The AFS allows to use folders and files, like in all common file systems, but with different connectors it is possible to use different solutions as the actual storage.
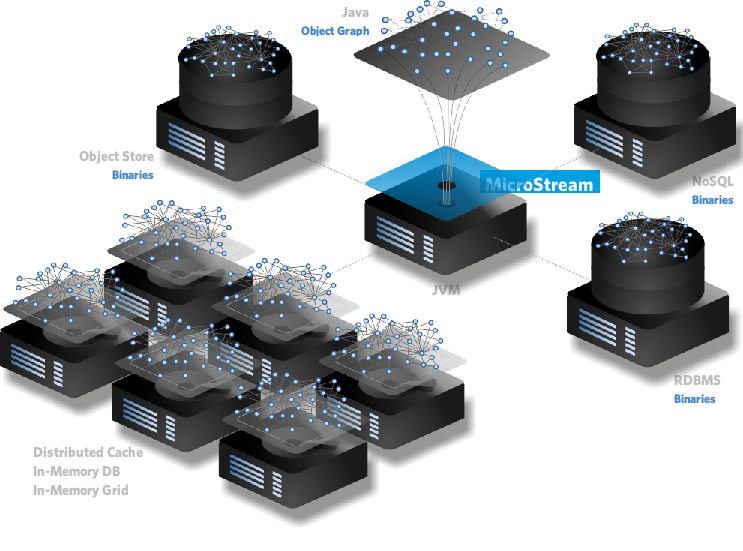
To connect to the local file system use the Java Non-Blocking IO (NIO) connector, which is part of the base module, so no additional dependency is needed.
EmbeddedStorage.start(Paths.get("path", "to", "storage"));Internally this creates and uses a NioFileSystem and is a shortcut for:
NioFileSystem fileSystem = NioFileSystem.New();
EmbeddedStorage.start(fileSystem.ensureDirectoryPath("path", "to", "storage"));The file system API is the same for all connectors, like for MySQL.
This is part of another module.
<!-- sql file system -->
<dependency>
<groupId>one.microstream</groupId>
<artifactId>microstream-enterprise-filesystem-sql</artifactId>
<version>06.01.00-MS-GA</version>
</dependency>
<!-- driver of your choice -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.21</version>
</dependency>// create JDBC data source
MysqlDataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://host:3306/mydb");
dataSource.setUser("user");
dataSource.setPassword("secret");
// create sql file system
SqlFileSystem fileSystem = SqlFileSystem.New(
// use caching connector
SqlConnector.Caching(
SqlProviderMySql.New(dataSource)
)
);
EmbeddedStorage.start(fileSystem.ensureDirectoryPath("path", "to", "storage"));